The Thyroid Goiter
What Is Thyroid Goiter?
Goiter is a swelling of the neck resulting from enlargement of the thyroid gland.
A goiter is an enlarged thyroid gland. The thyroid is the gland in front of the neck.
Goiter is the name given to a neck swelling produced by an abnormally enlarged thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is situated in front of the windpipe and is responsible for producing and secreting hormones that regulate growth and metabolism.
Goiters can be any one of several types of growths in the thyroid gland, located at the base of the front side of the neck just below the Adam's apple.
Causes of Thyroid Goiter
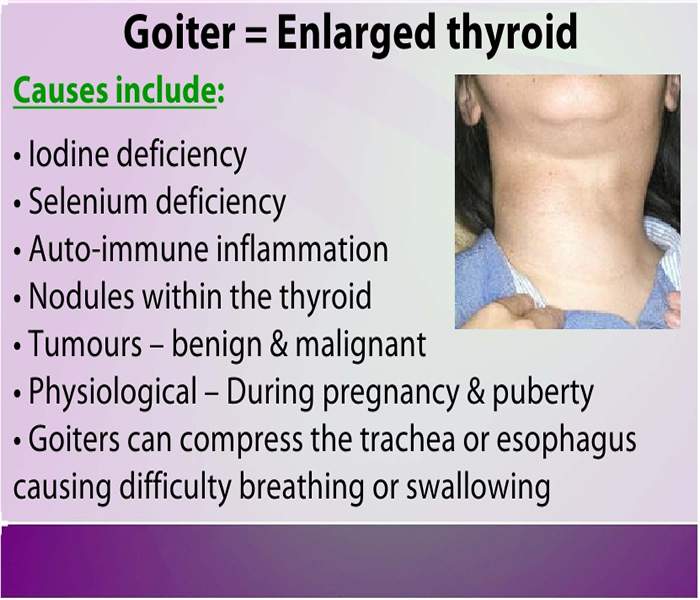
The major cause of goiter is Iodine deficiency. Goiter is rare in economically developed countries that add iodine to salt.
Goiters can also occur when the thyroid gland produces either too much thyroid hormone or not enough hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism respectively. The problem may arise when the pituitary gland stimulates thyroid growth to boost production of the hormone. Enlargement could also occur with normal production of thyroid hormone, such as a nontoxic multinodular gland.
As for developed countries the main cause of goiter is autoimmune disease. Women over the age of 40 are at greater risk of goiter.
Hypothyroidism is the result of an underactive thyroid gland, and this causes goiter.
Hypothyroidism is also a cause of goiter - from an overactive thyroid gland, which produces too much thyroid hormone.
The major cause of goiter is Iodine deficiency. Goiter is rare in economically developed countries that add iodine to salt.
Goiters can also occur when the thyroid gland produces either too much thyroid hormone or not enough hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism respectively. The problem may arise when the pituitary gland stimulates thyroid growth to boost production of the hormone. Enlargement could also occur with normal production of thyroid hormone, such as a nontoxic multinodular gland.
As for developed countries the main cause of goiter is autoimmune disease. Women over the age of 40 are at greater risk of goiter.
Hypothyroidism is the result of an underactive thyroid gland, and this causes goiter.
Hypothyroidism is also a cause of goiter - from an overactive thyroid gland, which produces too much thyroid hormone.
Rarely conditions that causes goiter are:
- Hormonal changes - pregnancy, puberty and the menopause can affect thyroid function
- Nodules - benign lumps, single or multiple
- Thyroiditis - inflammation caused by infection, for example
- Lithium - the psychiatric drug can interfere with thyroid function
- Overconsumption of iodine - Excess iodine can cause goiter
- Smoking - The content of tobacco called thiocyanate interferes with iodine absorption
- Radiation therapy - most especially if it is in the neck.
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty concentrating
- Difficulty swallowing(dysphagia)
- Dry cough and hoarseness
- Dry skin, nails and hair
- Drowsiness
- Fatigue
- Increased menstrual flow
- Throat tightness
- Visible swelling at the base of your neck
- Blood test
- Feeling the thyroid
- Thyroid scan
- Ultrasound
Symptoms/Signs of Thyroid Goiter
How to diagnose Thyroid Goiter
The most important part of diagnose goiter is the doctor's examination. Commonly the doctor will diagnose a goiter using some or all of the following techniques:
The most important part of diagnose goiter is the doctor's examination. Commonly the doctor will diagnose a goiter using some or all of the following techniques:
Feeling the Thyroid
By feeling the thyroid, the doctor can estimate the size of the gland, tell whether it is growing or not, and tell if it has any lumps in it that might be suspicious for cancer.
By feeling the thyroid, the doctor can estimate the size of the gland, tell whether it is growing or not, and tell if it has any lumps in it that might be suspicious for cancer.
Blood Test
Measurement of the levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and T4 in the blood stream are important because they help the doctor determine whether or not the goiter is making a normal amount of thyroid hormone. If the gland has a lump in it, the doctor may order a thyroid scan or an ultrasound to see if there are any masses in the thyroid that might be suspicious for a thyroid cancer.
Measurement of the levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and T4 in the blood stream are important because they help the doctor determine whether or not the goiter is making a normal amount of thyroid hormone. If the gland has a lump in it, the doctor may order a thyroid scan or an ultrasound to see if there are any masses in the thyroid that might be suspicious for a thyroid cancer.
Thyroid Scan
A thyroid scan is performed by having the patient take oral capsules that contain a harmless radioactive tracer (which is a tiny quantity of radioactive iodine). After four, six, or twenty-four hours (depending on the institution) a detector is placed over the thyroid gland. The amount of radioactive iodine that wound up in the thyroid gland is measured and a picture is taken of the distribution of radioactive iodine in the thyroid. In a normal thyroid gland, radioactive iodine is taken up to the same degree throughout the entire gland. If there is an area of the thyroid that does not take up radioactive iodine well, then it must be further investigated. The majority of these "cold" areas on a thyroid scan are benign, but about 5-10% of them are thyroid cancers. Under such circumstances an ultrasound might be ordered.
A thyroid scan is performed by having the patient take oral capsules that contain a harmless radioactive tracer (which is a tiny quantity of radioactive iodine). After four, six, or twenty-four hours (depending on the institution) a detector is placed over the thyroid gland. The amount of radioactive iodine that wound up in the thyroid gland is measured and a picture is taken of the distribution of radioactive iodine in the thyroid. In a normal thyroid gland, radioactive iodine is taken up to the same degree throughout the entire gland. If there is an area of the thyroid that does not take up radioactive iodine well, then it must be further investigated. The majority of these "cold" areas on a thyroid scan are benign, but about 5-10% of them are thyroid cancers. Under such circumstances an ultrasound might be ordered.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a way of taking a picture of the inside of the thyroid. Ultrasound bounces sound waves off the thyroid and makes a picture out of the returning echoes. If the ultrasound shows a large mass that is suspicious for cancer, then the ultrasonographer can use the ultrasound to guide a needle into the mass to perform a fine needle aspiration biopsy. If there are no large lumps in the thyroid gland that are suspicious for cancer, then no biopsy needs to be done. BY netwellness
Ultrasound is a way of taking a picture of the inside of the thyroid. Ultrasound bounces sound waves off the thyroid and makes a picture out of the returning echoes. If the ultrasound shows a large mass that is suspicious for cancer, then the ultrasonographer can use the ultrasound to guide a needle into the mass to perform a fine needle aspiration biopsy. If there are no large lumps in the thyroid gland that are suspicious for cancer, then no biopsy needs to be done. BY netwellness
How to Prevent Thyroid Goiter
Preventing simple goiter is as easy as a small change in diet. Iodine is necessary for producing thyroid hormones. Some patients do not eat enough iodine, so it causes the thyroid to work overtime to produce thyroid hormones. Using iodized table salt can prevent simple goiter.
Preventing simple goiter is as easy as a small change in diet. Iodine is necessary for producing thyroid hormones. Some patients do not eat enough iodine, so it causes the thyroid to work overtime to produce thyroid hormones. Using iodized table salt can prevent simple goiter.
READ MORE: Diet To Prevent Goiter






No comments:
Post a Comment